Net Zero powered by Pur și Simplu Verde provides concise news, articles, and useful information about the goal of achieving net zero emissions
Net zero refers to reaching an equilibrium between emitting greenhouse gases and absorbing them. The European Union wants to reach net zero (climate neutrality) by 2050. This website publishes new scientific discoveries, local and foreign initiatives, and public policies meant to bring us closer to net zero. It was created combining Artificial Intelligence and human input from our volunteers. It is accessible in both Romanian and in English.You can send us articles you want to see published on this site or suggestions here. Enjoy!
The combination of weak economic activity and the rise in extreme weather events is concerning. Typically, environmental pressures increase during economic booms, leading to surges in support for the green movement. This was observed in the early 1970s, late 1980s, and prior to the global financial crisis of 2008. The ongoing global heating despite slower economic growth is a significant cause for concern. The recent Canadian forest fires causing...
The European Space Agency (ESA) is working on the SOLARIS project, which aims to provide Europe with renewable energy from high-tech satellites in space, in response to the ongoing energy crisis caused by soaring fossil energy costs. ESA space-based solar panels would be capable to absorb and convert sunlight into energy 24 hours a day without being affected by earthly weather conditions. The satellites would wirelessly transmit power back to the planet. This ambitious project could potentially prevent future energy shortages and reduce dependence on costly large-scale energy storage solutions. The SOLARIS project, approved by the ESA Council in November of the previous year, will enter a phase of studies conducted over the next two and a half years in collaboration with the European industry. The studies will evaluate ...
In 2022, Denmark, Germany, Belgium, and the Netherlands held the first North Sea Summit in Esbjerg, Denmark. During the summit, the countries established the Esbjerg Declaration, setting ambitious goals for offshore wind power in the North Seas region. The aim is to transform the North Seas into a significant green power plant for Europe, contributing to climate neutrality and enhancing energy security in the region. In April 2023, the second North Sea Summit took place in Ostend, Belgium, with the participation of nine countries: Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Ireland, Luxembourg, Norway, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands. This summit aimed to unite their efforts in developing green energy in the North Seas, including the Atlantic Ocean, Irish Sea, and Celtic Sea. The countries will collaborate on deploying offshore wind projects and...
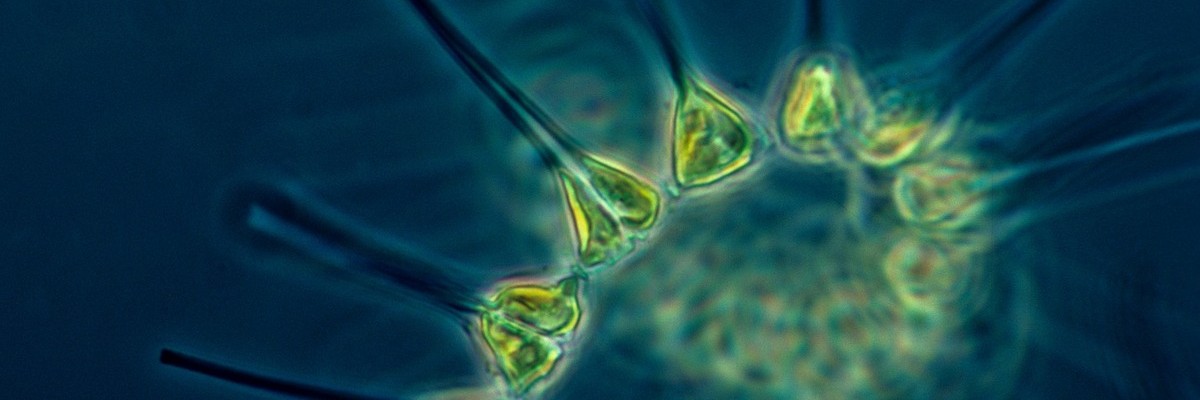
New research raises doubts about the energy efficiency of diesel alternatives derived from phytoplankton. Biodiesel derived from microalgae may actually emit more carbon during production and use than petroleum-based diesel. The poor performance of the biofuel is attributed to its manufacturing process, which requires more energy than the final product can generate. Microalgae, the phytoplankton that grows in fresh and saltwater, initially appeared as promising candidates for biofuel production, as they can produce up to 30 times more energy than other biofuels due to their high fat content. However, recent studies indicate that these advantages do not translate into energy efficiency due to the high costs and energy consumption associated with algae cultivation, processing, and electricity...
The movement to grant legal rights to rivers is gaining ground and drawing inspiration from indigenous perspectives on nature. In Chile and elsewhere, this movement challenges the traditional Western view of rivers and water as mere properties and rights held by corporations, disregarding the rights of ecosystems and human communities. In Chile, for example, the water code treats water as a renewable resource and allows the trading of water rights to the highest bidder. This has led to the degradation of many rivers and their ecosystems, as well as ongoing conflicts among different stakeholders. In some countries like New Zealand, Colombia, and India, steps have been taken to grant legal rights to rivers. For instance, in New Zealand, the Whanganui River has been granted the status of a legal person, while in Colombia, the Atrato River...
In the wilderness north of Great Slave Lake, in Canada's Northwest Territories, mining companies are turning their attention to a potential treasure trove of critical minerals as the demand for lithium, nickel, graphite, and copper has significantly increased to meet the needs of the emerging electric vehicle and solar energy industries. The cost of mining in these parts of Canada, with no access roads, was usually prohibitive. Things changed last December when the Canadian government announced its long-awaited Critical Minerals Strategy, offering mining companies generous tax incentives, additional funding incentives of $3 billion, and the promise to expedite the federal environmental impact assessment process. While the strategy is presented as a way to...
The ocean is a vital component of our ecosystem and harbors rich and diverse biodiversity. However, it faces numerous threats. Overfishing, rising ocean temperatures, pollution, and habitat destruction are just a few examples. To protect and restore the health of the ocean, an integrated and coordinated approach is necessary. One important aspect is the creation and effective management of protected areas. Currently, only a small portion of the ocean is legally protected. It is essential to conserve at least 30% of the ocean's surface through protected areas and other conservation mechanisms. These efforts may include establishing marine protected areas in regions with significant marine biodiversity and involving indigenous communities in their management. Additionally, promoting sustainable fishing and responsible management of marine resources is crucial. Overfishing poses a threat...
Decarbonization solutions in the maritime industry are at the center of debates, with a focus on the hybrid use of batteries and biodiesel. However, there are challenges and uncertainties regarding their implementation. For instance, ammonia, considered a potential fuel for the shipping industry, has unfavorable characteristics and potential environmental and human health risks. As for methanol, there are different production pathways, but the high costs and the need for widespread hydrogen use raise questions about its long-term viability. On the other hand, a strategic decarbonization model could involve the gradual implementation of batteries with increasing energy density for maritime vessels. In the coming years, battery technology will evolve significantly, allowing for greater autonomy for ships. For example, lithium-titanate batteries ...
Global investments in climate technology amount to $1.1 trillion. These major investments come from various sources and are directed towards startups developing innovative technologies to build a carbon-free future. Areas of interest include decarbonized food, carbon capture devices, futuristic materials, and next-generation fuels. Despite the significance of investments in solar panels and electric vehicles, investors are now focusing on other domains such as eco-friendly buildings, climate analytics, and carbon capture. In 2022, venture capital investments in climate technology reached a record level of $70.1 billion, marking a substantial increase compared to the previous year. This trend is supported by government, corporate, and consumer spending on emission reduction and climate adaptation...
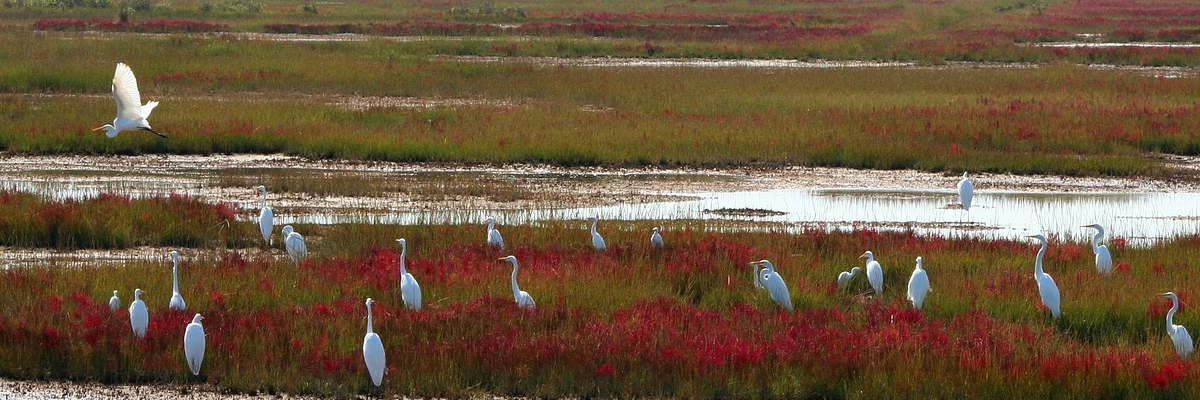
Researchers from the University of Cambridge and the nonprofit organization The Nature Conservancy have published the first global map of Earth's marshes. This is a significant achievement in ecosystem mapping and will enable countries to better understand the extent of marsh habitats along their coastlines and identify opportunities for conservation and restoration. Tidal marshes, considered 'blue carbon' ecosystems, are vital for human well-being, climate, and biodiversity, yet they have often been underestimated. The global map highlights that the Atlantic coasts of North America and Northern Europe are the global epicenters of tidal marshes, harboring 45% of the total. However, due to deforestation and drainage, tidal marsh areas have become rare, covering only 53,000 km2 globally. In comparison, mangroves cover nearly three times the area. The protection of remaining tidal marshes...